Security
Uncovering the Dark Side of Gemini AI: How Hackers are Exploiting it for Cyber Attacks

Reports indicate that state-sponsored hackers have been utilizing Google’s Gemini AI model at various stages of cyber attacks, ranging from initial reconnaissance to post-compromise activities.
Hackers from countries like China (including APT31 and Temp.HEX), Iran (APT42), North Korea (UNC2970), and Russia have been leveraging Gemini for tasks such as target profiling, open-source intelligence gathering, crafting phishing lures, language translation, coding, vulnerability testing, and troubleshooting.
There has been a noticeable uptick in cybercriminal interest in AI tools and services that can aid in illicit activities, including the execution of social engineering campaigns like ClickFix.

AI-Powered Malicious Operations
A recent report from the Google Threat Intelligence Group (GTIG) reveals that APT adversaries are harnessing Gemini AI to facilitate their campaigns, encompassing tasks from reconnaissance and phishing lure creation to command and control (C2) development and data exfiltration.
Chinese threat actors, for instance, employed Gemini to automate vulnerability analysis and devise targeted testing plans within a simulated scenario involving Remote Code Execution (RCE), WAF bypass techniques, and SQL injection tests against specific U.S.-based targets.
Another Chinese actor frequently utilized Gemini for code refinement, research purposes, and technical guidance related to intrusion activities.
The Iranian group APT42 leveraged Google’s LLM for social engineering campaigns and as a development platform to expedite the creation of tailored malicious tools, including debugging, code generation, and exploitation technique research.
Furthermore, there have been instances of threat actors enhancing existing malware families like the CoinBait phishing kit and the HonestCue malware downloader and launcher with AI capabilities.
GTIG highlights the emergence of HonestCue, a proof-of-concept malware framework that employs the Gemini API to generate C# code for second-stage malware and subsequently executes the payloads in memory.
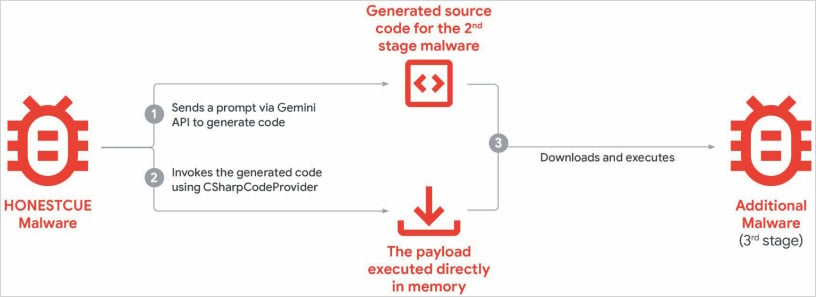
Source: Google
CoinBait, on the other hand, is a deceptive phishing kit disguised as a cryptocurrency exchange for harvesting credentials, with indications of AI code generation tool utilization in its development.
One telltale sign of LLM usage is the presence of logging messages prefixed with “Analytics:” in the malware source code, aiding defenders in tracking data exfiltration processes.
Based on malware samples, GTIG researchers infer that the Lovable AI platform was employed in creating the malware, as evidenced by the use of the Lovable Supabase client and lovable.app.
Cybercriminals have also leveraged generative AI services in ClickFix campaigns to distribute the AMOS info-stealing malware for macOS, enticing users to execute malicious commands through deceptive ads in search results related to troubleshooting specific issues.
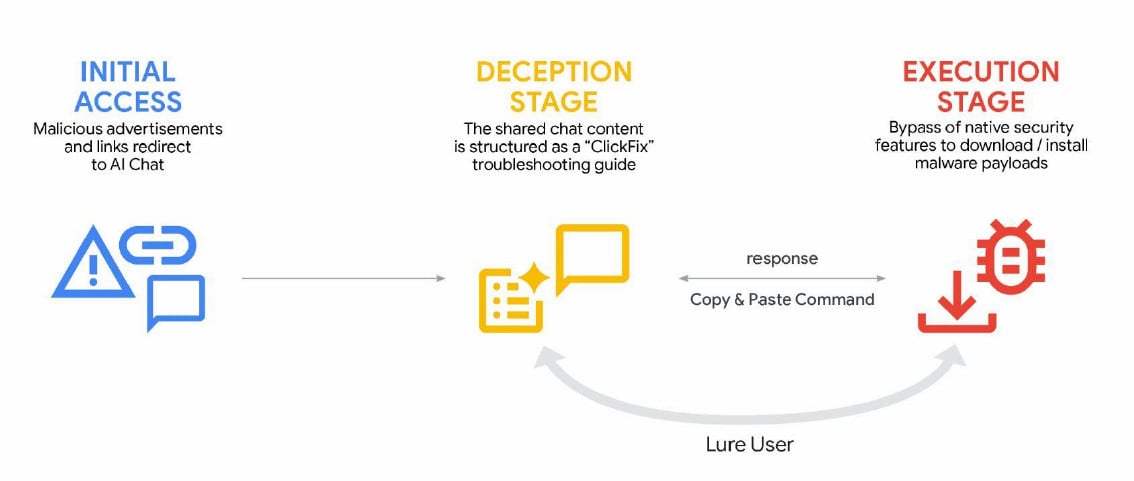
Source: Google
The report also highlights attempts at AI model extraction and distillation targeting Gemini, where entities exploit authorized API access to replicate the model’s decision-making processes for developing new models.
While not posing a direct risk to model users or data, this practice represents a significant commercial, competitive, and intellectual property challenge for the model creators.
Through knowledge distillation, attackers can expedite AI model development at a lower cost by transferring information from one model to another, a technique used to train new models based on existing ones.
Google identifies these attacks as intellectual property theft with scalability, posing a threat to the AI-as-a-service business model and potentially impacting end users in the future.
In a large-scale attack, Gemini AI was subjected to 100,000 prompts aimed at replicating the model’s decision-making across various tasks in non-English languages.
Google has taken measures to disable accounts and infrastructure linked to documented abuse and has enhanced defenses in Gemini’s classifiers to deter misuse.
The company emphasizes its commitment to designing AI systems with robust security measures and safety protocols, regularly testing models to enhance security and user safety.

Modern IT infrastructure outpaces manual workflows. Discover how your team can reduce delays, enhance reliability through automated responses, and build intelligent workflows leveraging existing tools in the comprehensive Tines guide.
-

 Facebook4 months ago
Facebook4 months agoEU Takes Action Against Instagram and Facebook for Violating Illegal Content Rules
-

 Facebook4 months ago
Facebook4 months agoWarning: Facebook Creators Face Monetization Loss for Stealing and Reposting Videos
-

 Facebook4 months ago
Facebook4 months agoFacebook Compliance: ICE-tracking Page Removed After US Government Intervention
-

 Facebook4 months ago
Facebook4 months agoInstaDub: Meta’s AI Translation Tool for Instagram Videos
-

 Facebook2 months ago
Facebook2 months agoFacebook’s New Look: A Blend of Instagram’s Style
-

 Facebook2 months ago
Facebook2 months agoFacebook and Instagram to Reduce Personalized Ads for European Users
-

 Facebook2 months ago
Facebook2 months agoReclaim Your Account: Facebook and Instagram Launch New Hub for Account Recovery
-

 Apple4 months ago
Apple4 months agoMeta discontinues Messenger apps for Windows and macOS































