Security
Google Patches Critical Zero-Day Exploit in Chrome, First Attack of the Year

Google Chrome Vulnerability Patched in Emergency Update
Google recently released emergency updates to address a high-severity vulnerability in Chrome that was being exploited in zero-day attacks. This marks the first security flaw patched since the beginning of the year.
According to a security advisory issued by Google, the company is aware of the existence of an exploit for CVE-2026-2441 in the wild.
The vulnerability, reported by security researcher Shaheen Fazim, is a use-after-free vulnerability caused by an iterator invalidation bug in CSSFontFeatureValuesMap, which is Chrome’s implementation of CSS font feature values. Exploiting this flaw could lead to browser crashes, rendering issues, data corruption, or other unpredictable behaviors.
The patch for CVE-2026-2441 addresses the immediate problem, but additional work is needed as indicated by the Chromium commit history. It appears that there are remaining issues tracked in bug 483936078, suggesting that further fixes might be required.
The patch was labeled as “cherry-picked,” indicating its importance, and it was backported across multiple commits to ensure it was included in a stable release promptly due to the active exploitation of the vulnerability.
While Google confirmed that attackers were exploiting this zero-day flaw, they did not disclose specific details about these incidents.
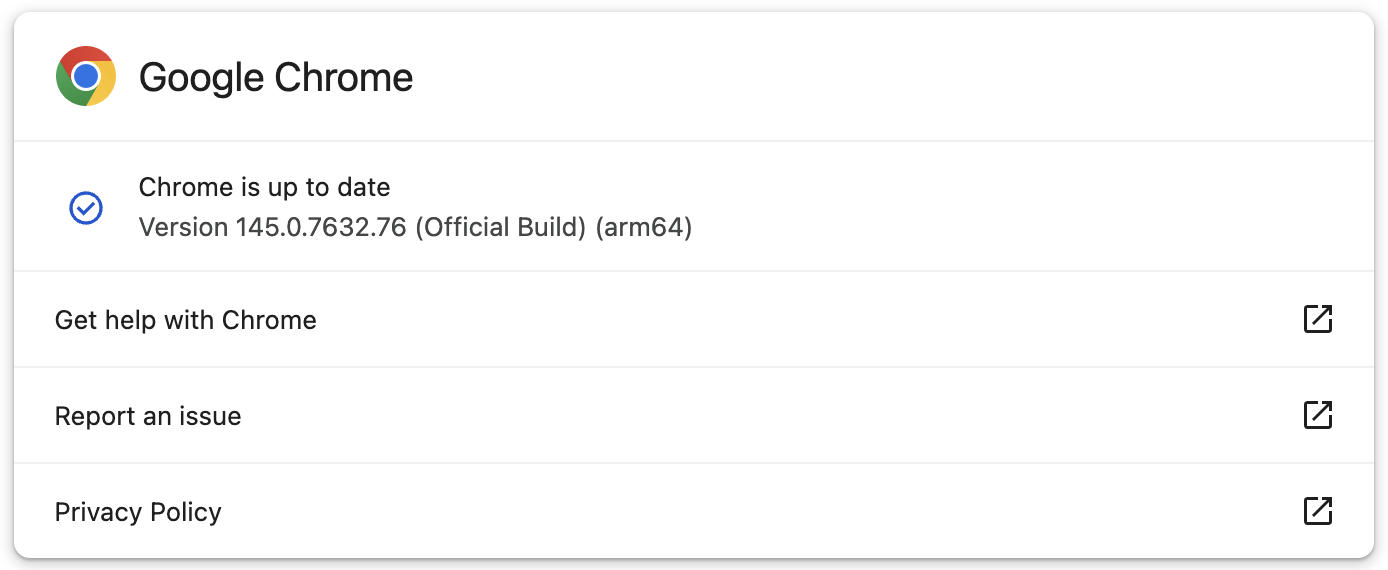
Google has already rolled out the fix for this vulnerability to users in the Stable Desktop channel, with new versions being distributed to Windows, macOS (145.0.7632.75/76), and Linux users (144.0.7559.75) worldwide in the coming days.
For users who prefer not to manually update, Chrome can automatically check for updates and install them upon the next launch.
This is the first actively exploited Chrome security vulnerability patched in 2026. In the previous year, Google addressed a total of eight zero-day vulnerabilities that were being exploited in the wild, many of which were reported by the Threat Analysis Group (TAG) known for identifying zero-days used in spyware attacks targeting high-risk individuals.

Modern IT infrastructure moves faster than manual workflows can handle.
In this new Tines guide, discover how your team can reduce hidden manual delays, enhance reliability through automated response, and create and scale intelligent workflows using tools you already use.
-

 Facebook4 months ago
Facebook4 months agoEU Takes Action Against Instagram and Facebook for Violating Illegal Content Rules
-

 Facebook4 months ago
Facebook4 months agoWarning: Facebook Creators Face Monetization Loss for Stealing and Reposting Videos
-

 Facebook4 months ago
Facebook4 months agoFacebook Compliance: ICE-tracking Page Removed After US Government Intervention
-

 Facebook4 months ago
Facebook4 months agoInstaDub: Meta’s AI Translation Tool for Instagram Videos
-

 Facebook2 months ago
Facebook2 months agoFacebook’s New Look: A Blend of Instagram’s Style
-

 Facebook2 months ago
Facebook2 months agoFacebook and Instagram to Reduce Personalized Ads for European Users
-

 Facebook2 months ago
Facebook2 months agoReclaim Your Account: Facebook and Instagram Launch New Hub for Account Recovery
-

 Apple4 months ago
Apple4 months agoMeta discontinues Messenger apps for Windows and macOS































