Security
Rampant Vulnerabilities: The Alarming Risks of Exposed Telnet Servers

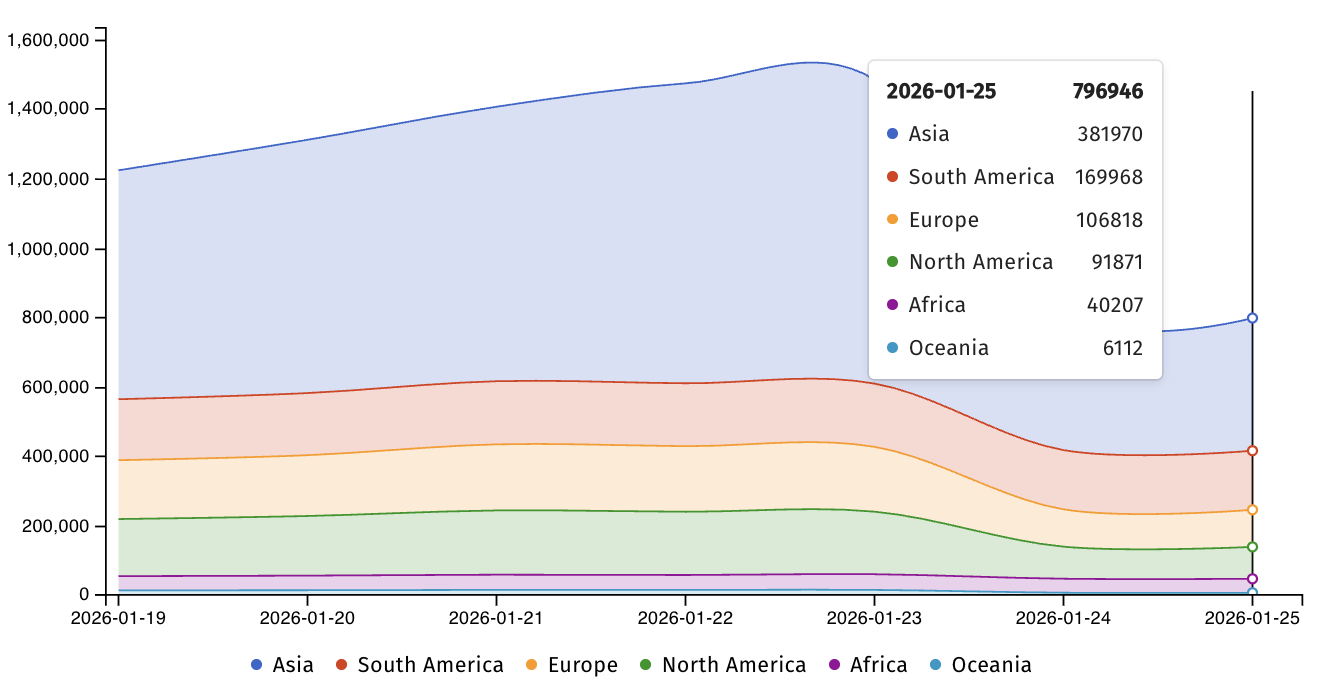
Recent Telnet Vulnerability Exposes Nearly 800,000 IP Addresses to Attacks
A critical authentication bypass vulnerability in the GNU InetUtils telnetd server has put nearly 800,000 IP addresses at risk, according to internet security watchdog Shadowserver. The flaw, identified as CVE-2026-24061, affects GNU InetUtils versions 1.9.3 through 2.7 and was only recently patched in version 2.8.
Open-source contributor Simon Josefsson, who reported the security flaw, explained that the telnetd server could be exploited by supplying a carefully crafted USER environment value to bypass normal authentication processes. This loophole allows attackers to automatically log in as root without the need for proper credentials.
Shadowserver reported that they are currently monitoring around 800,000 IP addresses with Telnet fingerprints, with a significant number originating from Asia, South America, and Europe. Despite this, it remains unclear how many of these devices have been secured against the CVE-2026-24061 attacks.
CEO Piotr Kijewski of Shadowserver Foundation emphasized the importance of securing telnet instances globally, especially on legacy IoT devices. Telnet, being a legacy protocol, should not be publicly exposed, but it often is, leading to potential security risks.
GNU InetUtils, a collection of network utilities used in multiple Linux distributions, including telnet/telnetd, ftp/ftpd, rsh/rshd, ping, and traceroute, has been found to run on many legacy and embedded devices without updates for over a decade. This prolonged use explains its presence in IoT devices, as highlighted by Kijewski.
Following the disclosure of CVE-2026-24061, cybersecurity company GreyNoise detected limited attacks exploiting the vulnerability. These attacks, originating from 18 IP addresses across 60 Telnet sessions, utilized the Telnet IAC option negotiation to gain shell access to compromised devices without authentication.
While most of the attacks targeted the ‘root’ user, GreyNoise noted some variations in terminal speed and X11 DISPLAY values. Despite automated characteristics, some attacks showed signs of manual intervention, indicating a mix of automated and human-driven exploitation.
After gaining access, attackers attempted to deploy Python malware on compromised devices, but their efforts were thwarted due to missing directories and binaries necessary for the malware to execute successfully.
For administrators unable to immediately update their devices with the patched release, experts recommend disabling the vulnerable telnetd service or blocking TCP port 23 on all firewalls to mitigate the risk of exploitation.

As organizations plan their cybersecurity budgets for the upcoming year, insights from over 300 CISOs and security leaders can provide valuable guidance. Learn how top leaders are prioritizing investments to drive measurable impact in 2026.
Download the exclusive report now to benchmark strategies and identify emerging trends.
-

 Facebook4 months ago
Facebook4 months agoEU Takes Action Against Instagram and Facebook for Violating Illegal Content Rules
-

 Facebook4 months ago
Facebook4 months agoWarning: Facebook Creators Face Monetization Loss for Stealing and Reposting Videos
-

 Facebook4 months ago
Facebook4 months agoFacebook Compliance: ICE-tracking Page Removed After US Government Intervention
-

 Facebook4 months ago
Facebook4 months agoInstaDub: Meta’s AI Translation Tool for Instagram Videos
-

 Facebook2 months ago
Facebook2 months agoFacebook’s New Look: A Blend of Instagram’s Style
-

 Facebook2 months ago
Facebook2 months agoFacebook and Instagram to Reduce Personalized Ads for European Users
-

 Facebook2 months ago
Facebook2 months agoReclaim Your Account: Facebook and Instagram Launch New Hub for Account Recovery
-

 Apple4 months ago
Apple4 months agoMeta discontinues Messenger apps for Windows and macOS
































