Security
Ivanti raises alarm over critical Endpoint Manager vulnerability

Ivanti Warns Customers of Critical Vulnerability in Endpoint Manager Solution
An urgent alert has been issued by American IT software company Ivanti regarding a newly disclosed vulnerability in its Endpoint Manager (EPM) solution. This vulnerability poses a significant risk as it could potentially allow attackers to remotely execute malicious code.
Ivanti, a leading provider of system and IT asset management solutions, caters to over 40,000 companies globally through a network of more than 7,000 organizations. Their EPM software serves as a comprehensive endpoint management tool, enabling the management of client devices across various popular platforms, including Windows, macOS, Linux, Chrome OS, and IoT.
The identified security flaw, known as CVE-2025-10573, is classified as critical and can be exploited by remote threat actors without authentication. These attackers can execute arbitrary JavaScript code through low-complexity cross-site scripting attacks that necessitate user interaction.
Ryan Emmons, a security researcher at Rapid7, who reported the vulnerability in August, explained, “An attacker with unauthenticated access to the primary EPM web service can join fake managed endpoints to the EPM server in order to poison the administrator web dashboard with malicious JavaScript. When an Ivanti EPM administrator views one of the poisoned dashboard interfaces during normal usage, that passive user interaction will trigger client-side JavaScript execution, resulting in the attacker gaining control of the administrator’s session.”
To address this critical issue, Ivanti has released EPM version EPM 2024 SU4 SR1. They have also highlighted that the risk associated with this vulnerability should be significantly mitigated as the Ivanti EPM solution is not designed to be exposed online.
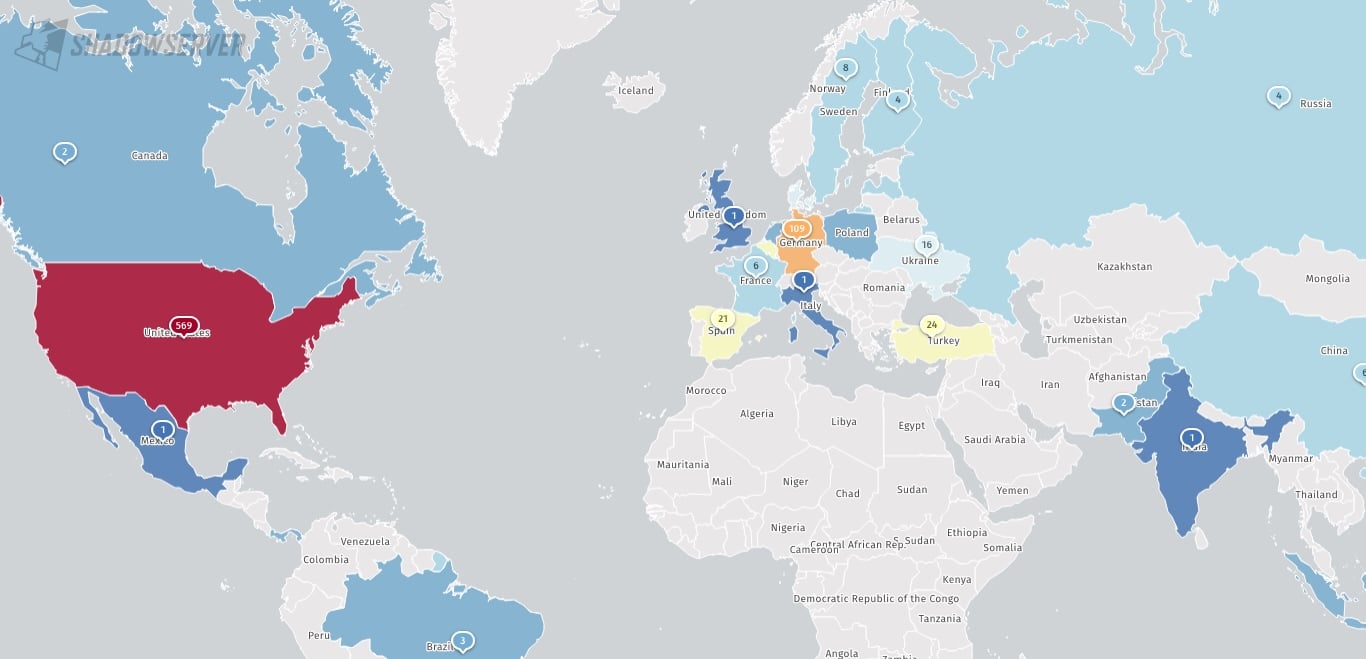
Despite this precaution, the Shadowserver threat monitoring platform has identified numerous Internet-facing Ivanti EPM instances, with a majority located in the United States (569), Germany (109), and Japan (104).
Additionally, Ivanti has released security updates to address three high-severity vulnerabilities, two of which (CVE-2025-13659 and CVE-2025-13662) have the potential to enable unauthenticated attackers to execute arbitrary code on unpatched systems.
Fortunately, successful exploitation of these vulnerabilities also requires user interaction, with targets needing to connect to an untrusted core server or import untrusted configuration files.
According to Ivanti, “We are not aware of any customers being exploited by these vulnerabilities prior to public disclosure. These vulnerabilities were disclosed through our responsible disclosure program.”
Despite no reported cases of exploitation, Ivanti acknowledges that their EPM security flaws are often targeted by threat actors. Earlier this year, in March, CISA flagged three critical vulnerabilities affecting EPM appliances (CVE-2024-13159, CVE-2024-13160, and CVE-2024-13161) as exploited in attacks, prompting U.S. federal agencies to secure their networks within a three-week timeframe.
Furthermore, the U.S. cybersecurity agency directed government agencies to patch an actively exploited EPM flaw (CVE-2024-29824) in October 2024.

Addressing broken IAM is crucial as it impacts the entire business, not just IT.
Discover why traditional IAM practices fall short in modern environments, explore examples of effective IAM strategies, and access a simple checklist for developing a scalable approach.
-

 Facebook4 months ago
Facebook4 months agoEU Takes Action Against Instagram and Facebook for Violating Illegal Content Rules
-

 Facebook4 months ago
Facebook4 months agoWarning: Facebook Creators Face Monetization Loss for Stealing and Reposting Videos
-

 Facebook4 months ago
Facebook4 months agoFacebook Compliance: ICE-tracking Page Removed After US Government Intervention
-

 Facebook4 months ago
Facebook4 months agoInstaDub: Meta’s AI Translation Tool for Instagram Videos
-

 Facebook2 months ago
Facebook2 months agoFacebook’s New Look: A Blend of Instagram’s Style
-

 Facebook2 months ago
Facebook2 months agoFacebook and Instagram to Reduce Personalized Ads for European Users
-

 Facebook2 months ago
Facebook2 months agoReclaim Your Account: Facebook and Instagram Launch New Hub for Account Recovery
-

 Apple4 months ago
Apple4 months agoMeta discontinues Messenger apps for Windows and macOS































