Inovation
Revolutionizing Biomechanics: Unleashing the Power of Highly Accurate Digital Twins
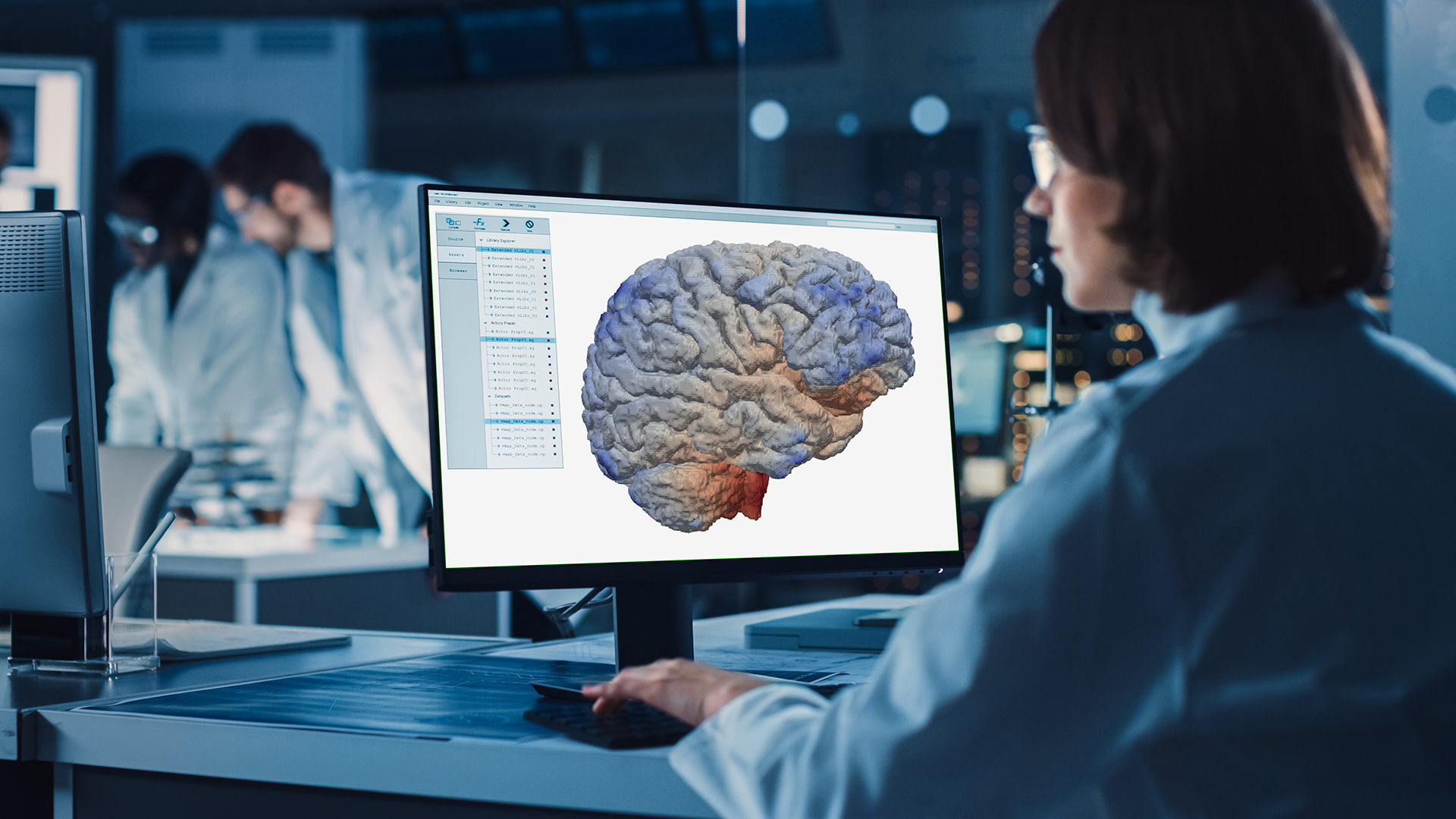
The dealii-X project is dedicated to creating precise digital replicas of human organs using advanced computational models to enhance biomechanical insights and improve medical understanding and treatment of diseases.
The project, known as “dealii-X: an Exascale Framework for Digital Twins of the Human Body,” is part of the EuroHPC Centres of Excellence. Its goal is to develop a scalable computational platform for creating accurate digital twins of human organs. The project heavily relies on the deal.II library, a toolbox that facilitates the rapid development of finite element models for solving partial differential equations. These models have traditionally been used in various engineering problems, such as heat distribution, structural mechanics, and sound propagation.
The dealii-X project aims to apply this successful approach to biomechanics, specifically in creating accurate models of human organs like the lungs, heart, brain, liver, and cell mobility processes. While computational models in biomedicine are not new, most of them have been limited in scope and quality. With advancements in computing capabilities and mathematical modeling, dealii-X seeks to develop comprehensive models that closely replicate the processes within human organs.
One of the key challenges in setting up these models is the variability in organ configurations among individuals and the continuous remodeling of organs throughout a person’s lifetime. This necessitates meticulous data collection to create accurate organ geometries, while still leaving many aspects uncertain. Additionally, modeling organs accurately requires considering a wide range of scales, from cellular processes to tissue layers, where different mechanical phenomena interact.
The dealii-X project leverages exascale computing capabilities to model complex biological processes at an unprecedented level of detail. The project officially commenced in October 2024, with initial results starting to emerge. Researchers from Germany, Italy, France, and Belgium are collaborating to develop advanced models in the dealii-X consortium.
One area of focus within the project is respiratory mechanics, particularly in understanding the effects of mechanical ventilation on lung tissue. Computational models offer insights into how different ventilation strategies impact patient-specific lung geometries, which are challenging to observe directly through medical imaging.
In cardiovascular simulations, dealii-X researchers in Italy are introducing a matrix-free computational framework for efficient large-scale simulations. This approach computes operations on the fly, reducing memory usage and communication overhead, thereby enhancing computational efficiency and resource utilization.
Understanding the biomechanical properties of the human brain is crucial for improving the diagnosis and treatment of brain-related conditions. The ExaBrain project, developed by researchers in Germany, aims to create detailed models of brain tissue mechanics to assist in preoperative planning and surgical procedures.
Cell motility and interactions are fundamental in processes like tumor metastasis and embryogenesis. The dealii-X project includes the development of novel continuum multiphysics models to study cellular motility. Researchers in Italy are working on software to advance cellular investigations and support mechanobiological research.
Overall, the dealii-X project showcases a diverse range of models and developments in the field of computational biomechanics. By leveraging large-scale computing resources, researchers are pushing the boundaries of what is achievable in biomedical applications. The interdisciplinary nature of the project allows for cross-disciplinary learning and innovation, with the potential for impactful discoveries and advancements in various fields beyond biomedicine.
-

 Facebook4 months ago
Facebook4 months agoEU Takes Action Against Instagram and Facebook for Violating Illegal Content Rules
-

 Facebook4 months ago
Facebook4 months agoWarning: Facebook Creators Face Monetization Loss for Stealing and Reposting Videos
-

 Facebook4 months ago
Facebook4 months agoFacebook Compliance: ICE-tracking Page Removed After US Government Intervention
-

 Facebook4 months ago
Facebook4 months agoInstaDub: Meta’s AI Translation Tool for Instagram Videos
-

 Facebook2 months ago
Facebook2 months agoFacebook’s New Look: A Blend of Instagram’s Style
-

 Facebook2 months ago
Facebook2 months agoFacebook and Instagram to Reduce Personalized Ads for European Users
-

 Facebook2 months ago
Facebook2 months agoReclaim Your Account: Facebook and Instagram Launch New Hub for Account Recovery
-

 Apple4 months ago
Apple4 months agoMeta discontinues Messenger apps for Windows and macOS