Security
The Dominance of a Single Threat Actor in Ivanti RCE Attacks

One Threat Actor Responsible for 83% of Recent Ivanti RCE Attacks
Recent threat intelligence indicates that a single threat actor is behind the majority of active exploitation of critical vulnerabilities in Ivanti Endpoint Manager Mobile (EPMM), specifically CVE-2026-21962 and CVE-2026-24061.
These vulnerabilities have been actively exploited in zero-day attacks, prompting Ivanti to issue security advisories and provide hotfixes to address the issues.
Both vulnerabilities have been classified as critical, allowing attackers to execute code without authentication, potentially leading to remote code execution (RCE) on vulnerable systems.

An IP address hosted on bulletproof infrastructure has been identified as the source of over 83% of exploitation activities related to these vulnerabilities, according to GreyNoise, a threat-focused internet intelligence company.
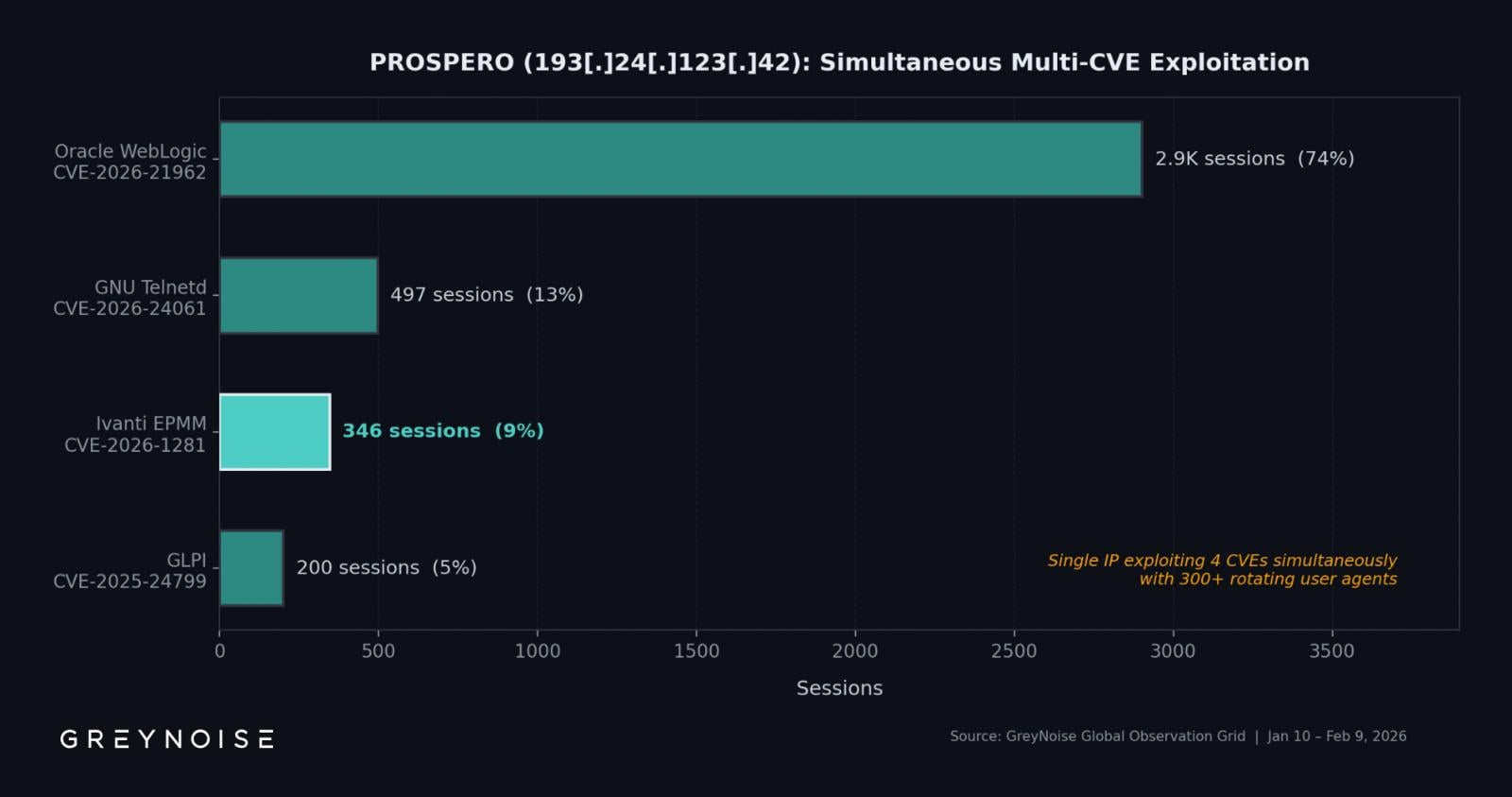
Between February 1st and 9th, GreyNoise observed 417 exploitation sessions originating from 8 unique source IP addresses, primarily targeting CVE-2026-21962 and CVE-2026-24061.
On February 8, a significant spike occurred with 269 recorded sessions in a single day, nearly 13 times the daily average. The majority of the exploitation sessions utilized OAST-style DNS callbacks to validate command execution capability, indicating initial access broker activity.
Interestingly, while some indicators of compromise (IoCs) include IP addresses associated with Windscribe VPN, no Ivanti exploitation activity was detected. This suggests that defenders relying solely on published indicators may overlook the primary source of exploitation.
The identified IP address was not limited to targeting Ivanti, as it also exploited vulnerabilities in Oracle WebLogic, GNU Inetutils Telnetd, and GLPI simultaneously.
While Ivanti has released fixes for CVE-2026-1281 and CVE-2026-1340, the company plans to issue complete patches with the release of EPMM version 12.8.0.0 in the first quarter of this year.
Until then, users are advised to utilize specific RPM packages based on their EPMM versions and consider building a replacement instance for enhanced security.
Source: GreyNoise
Analysis of the exploitation activity reveals a highly automated process utilizing a variety of user agents and focusing on multiple vulnerabilities across different software products.

Modern IT infrastructure moves faster than manual workflows can handle.
Discover how your team can reduce delays, improve reliability, and scale workflows with automated responses in the new Tines guide.
-

 Facebook4 months ago
Facebook4 months agoEU Takes Action Against Instagram and Facebook for Violating Illegal Content Rules
-

 Facebook4 months ago
Facebook4 months agoWarning: Facebook Creators Face Monetization Loss for Stealing and Reposting Videos
-

 Facebook4 months ago
Facebook4 months agoFacebook Compliance: ICE-tracking Page Removed After US Government Intervention
-

 Facebook4 months ago
Facebook4 months agoInstaDub: Meta’s AI Translation Tool for Instagram Videos
-

 Facebook2 months ago
Facebook2 months agoFacebook’s New Look: A Blend of Instagram’s Style
-

 Facebook2 months ago
Facebook2 months agoFacebook and Instagram to Reduce Personalized Ads for European Users
-

 Facebook2 months ago
Facebook2 months agoReclaim Your Account: Facebook and Instagram Launch New Hub for Account Recovery
-

 Apple4 months ago
Apple4 months agoMeta discontinues Messenger apps for Windows and macOS































