Security
Exploiting Triofox Antivirus: How Hackers Use Remote Access Tools

Cybercriminals have taken advantage of a critical vulnerability and the integrated antivirus feature in Gladinet’s Triofox file-sharing and remote access platform to execute remote code with SYSTEM privileges.
The vulnerability exploited in the attack is known as CVE-2025-12480, enabling hackers to bypass authentication and gain entry to the application’s setup pages.
Security experts from Google Threat Intelligence Group (GTIG) uncovered this malicious activity on August 24 when a threat group identified as UNC6485 targeted a Triofox server operating on version 16.4.10317.56372, which was released on April 3.

The vulnerability identified as CVE-2025-12480 stems from an access control flaw where admin privileges are granted if the application’s request URL host matches ‘localhost’.
This loophole allows attackers to manipulate this value through the HTTP Host header and circumvent all authentication protocols.
Mandiant elaborates that in the absence of the optional TrustedHostIp parameter in web.config, the ‘localhost’ verification becomes the sole gatekeeper, leaving default installations vulnerable to unauthorized access.
A patch for CVE-2025-12480 was introduced in Triofox version 16.7.10368.56560, released on July 26, and GTIG researchers verified with the vendor that the vulnerability had been rectified.
Exploiting the antivirus feature
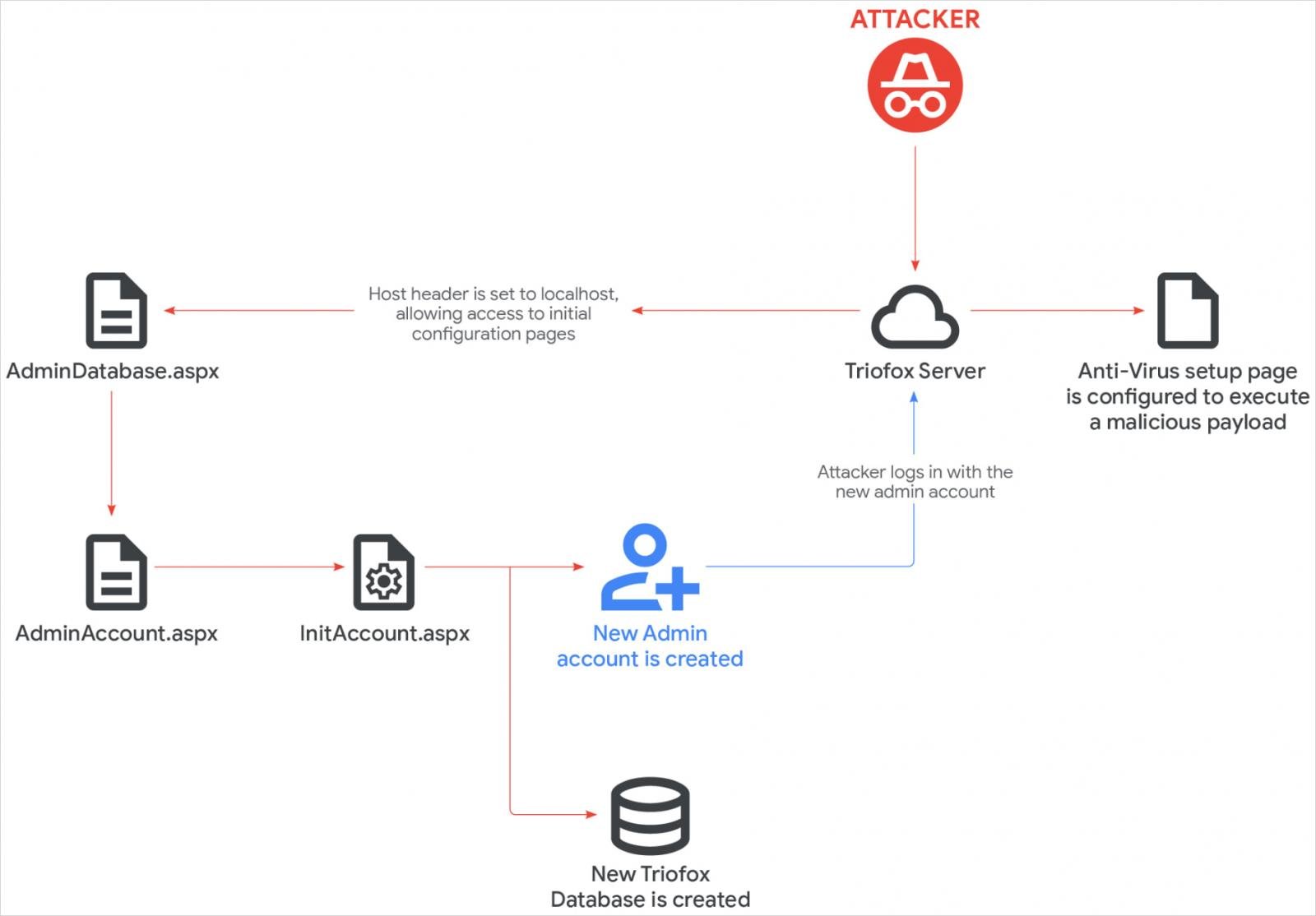
Mandiant’s investigation revealed that UNC6485 exploited the vulnerability by sending an HTTP GET request with ‘localhost’ in the HTTP Referer URL.
“The presence of the localhost host header in a request originating from an external source is highly irregular and typically not expected in legitimate traffic,” the researchers explain.
This granted them access to the AdminDatabase.aspx configuration page, used for setting up Triofox post-installation.
Through the setup process, the attacker created a new admin account named ‘Cluster Admin’ and utilized it to upload a malicious script, configuring Triofox to designate its path as the antivirus scanner’s location.
GTIG highlights that “the file designated as the antivirus scanner inherits the privileges of the Triofox parent process account, operating under the SYSTEM account context,” facilitating code execution.
The malicious batch executed a PowerShell downloader to retrieve another payload, a Zoho UEMS installer, from an external source.
Source: Google
Zoho UEMS was utilized to deploy Zoho Assist and AnyDesk on the compromised host, enabling remote access and lateral movement activities.
The attackers also leveraged Plink and PuTTY tools to establish an SSH tunnel and redirect remote traffic to the host’s RDP port (3389).

Source: Google
Although the CVE-2025-12480 vulnerability was addressed in Triofox 16.7.10368.56560, Mandiant recommends system administrators to apply the latest security update available in version 16.10.10408.56683, released on October 14.
Another suggestion is to review admin accounts and ensure that Triofox’s antivirus engine is not configured to run unauthorized scripts or binaries.
GTIG’s report includes a list of indicators of compromise (IoCs) to assist defenders in thwarting such attacks, with detailed information accessible on VirusTotal.
Recently, Huntress reported instances of hackers exploiting a zero-day local file inclusion vulnerability (CVE-2025-11371) in Gladinet CentreStack and Triofox products to access system files without authentication.
This flaw, utilized in at least three successful network intrusions, was promptly addressed in the latest version 16.10.10408.56683.

As MCP (Model Context Protocol) becomes the standard for connecting LLMs to tools and data, security teams are moving fast to keep these new services safe.
This free cheat sheet outlines 7 best practices you can start using today.
-

 Facebook4 months ago
Facebook4 months agoEU Takes Action Against Instagram and Facebook for Violating Illegal Content Rules
-

 Facebook4 months ago
Facebook4 months agoWarning: Facebook Creators Face Monetization Loss for Stealing and Reposting Videos
-

 Facebook4 months ago
Facebook4 months agoFacebook Compliance: ICE-tracking Page Removed After US Government Intervention
-

 Facebook4 months ago
Facebook4 months agoInstaDub: Meta’s AI Translation Tool for Instagram Videos
-

 Facebook2 months ago
Facebook2 months agoFacebook’s New Look: A Blend of Instagram’s Style
-

 Facebook2 months ago
Facebook2 months agoFacebook and Instagram to Reduce Personalized Ads for European Users
-

 Facebook2 months ago
Facebook2 months agoReclaim Your Account: Facebook and Instagram Launch New Hub for Account Recovery
-

 Apple4 months ago
Apple4 months agoMeta discontinues Messenger apps for Windows and macOS